The European Union's (EU) Artificial Intelligence (AI) Act mandates human oversight of AI systems, particularly those classified as high-risk, to ensure that they operate ethically, transparently, and safely. CloudFactory fulfills this critical requirement, offering specialized services that integrate human oversight directly into AI workflows, thereby aligning with the EU's legislative framework and enhancing the reliability and accountability of AI technologies.
Introducing the EU AI Act
In March 2024, the AI Act was introduced by the EU as a major legislative milestone in the regulation of artificial intelligence. The AI Act divides the application of AI technology into categories of perceived risk, ranging from “unacceptable”—which would see the technology banned—to high and medium to low.
This risk-based approach can be explained in more detail as follows:
- Unacceptable risk: The Act bans AI systems considered a clear threat to people's safety, livelihoods, and rights. This includes manipulative AI that exploits vulnerabilities of specific groups, real-time biometric identification systems in public spaces (with certain exceptions for law enforcement), social scoring systems by governments, and AI that enables 'predictive policing'.
- High-risk: AI systems used in critical areas like healthcare, policing, transportation, and education that will be subject to stringent requirements before they can be introduced. These requirements include strict levels of transparency (about use), accuracy (of outcomes), and security (of the system).
- Medium (limited) and low (minimal) risk: The AI Act imposes minimal new obligations on providers for AI applications with medium or low risk, such as AI-enabled video games or spam filters. For example, businesses utilizing chatbots must disclose that they are AI-driven to ensure end-users are aware and kept fully informed.
The AI Act proposes significant fines for non-compliance, up to 6% of an entity's total worldwide annual turnover for the most severe infringements, which is more punitive than the EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
The proposed enforcement mechanism is designed to ensure that AI system providers are developing and deploying their solutions in a way that is ethical, secure, and respects the fundamental rights of individuals.
Who will the AI Act impact?
Although the AI Act is an EU regulation, its impact is expected to be felt globally, given that many businesses seek to deploy multi-jurisdictional products and services.
Non-EU-based companies that offer AI products or services to, or accessible by citizens of the EU will need to comply, making it a global benchmark standard for AI regulation.
Those in the UK, the United States, Canada, and elsewhere will need to be mindful of this while also keeping a close eye on developments of AI regulation in their own country.
What this means for AI business leaders
Overall, the EU AI Act represents a significant shift towards greater regulation of AI, with profound implications for businesses involved in AI across various sectors. Companies have a limited window of time before the AI Act is finalized and enforceable to allow them to proactively adjust their strategies and operations as needed to align with these new requirements.
On the plus side, the new regulatory environment will also give clearer guidance for those exploring opportunities for innovation and competitive differentiation within a regulated environment.
As with other types of regulation, including the EU’s GDPR, businesses can expect to see increased compliance costs and efforts if providing high-risk AI systems including obligations to maintain detailed documentation and risk assessments, while strict governance will become front-and-center in product design and corporate decision-making.
Businesses must enhance transparency and data governance, ensuring AI systems use lawfully obtained data. Otherwise, they will face higher liability and legal risks for non-compliance, which, if not addressed sufficiently, could lead to fines and reputational damage.
Demonstrating adherence to the AI Act can also offer a competitive advantage, bolstering a company's reputation in trust-sensitive markets. These are just some call-outs of the pros and cons implications that business leaders can expect to face.
One thing is for sure: its global impact suggests a shift in focus to managing a multi-jurisdictional model of AI regulatory standards worldwide. This will prompt companies to consider risk mitigation, through transfer, by forming strategic partnerships and collaborations that help with navigation of compliance complexities, leveraging external expertise for both one-off projects and ongoing conformance within a regulated environment.
Diving deeper into high-risk
The bar has been set for any businesses considering products and services that meet the definition of the "high-risk" category of AI applications, as defined by the AI Act. However, further guidance is anticipated in the months ahead.
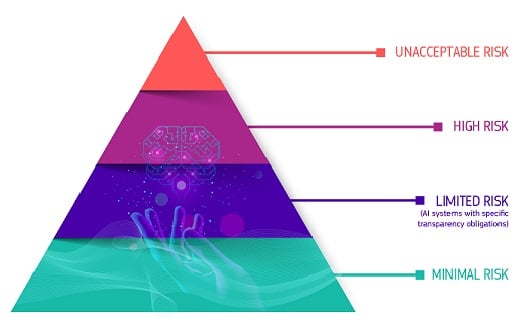
The above Regulatory Framework defines 4 levels of risk for AI systems. Source: European Commission
High-risk applications require adherence to stringent regulatory requirements, including transparency, data governance, human oversight, and robustness. The concerns are primarily due to the potential for significant adverse impacts on individuals' rights or safety if these AI systems fail or are misused.
Compliance with these regulations ensures that AI systems are trustworthy and potential risks are managed effectively. Still, it also means that businesses must invest more in risk assessment, compliance measures, and ongoing monitoring.

It’s important for any company impacted by this AI Act to understand and follow key obligations for high-risk AI. These include:
- Data governance and management: Ensures that training, validation, and testing of data are done in a manner that respects EU values, aiming for high accuracy and security.
- Technical documentation and record-keeping: Entities must maintain detailed documentation of their AI systems to demonstrate compliance with the AI Act.
- Transparency and provision of information to users: Users should be informed about an AI system's capabilities, purpose, and limitations.
- Accuracy, robustness, and security: High-risk AI systems must be secure, accurate, and resilient against both intentional and unintentional manipulation.
- Human oversight: AI systems should be designed to include effective human oversight to prevent or minimize risks.
So, for businesses operating or developing AI systems within these high-risk areas, there's a critical need to focus on aspects such as:
- Ensuring that AI systems are transparent and explainable allows users and affected parties to understand how decisions are made.
- Given the sensitivity of the information often involved, stringent data protection measures must be implemented to secure the data used by AI systems.
- Establishing effective human oversight mechanisms to monitor AI decision-making and intervene when necessary to prevent harm.
- Conducting thorough risk assessments and audits to identify and mitigate potential adverse impacts on individuals and society.
CloudFactory delivers accuracy, robustness, and security – with the right level of human oversight
CloudFactory’s security capabilities can significantly assist with meeting the EU’s AI Act’s requirements for accuracy, robustness, and security in high-risk AI systems. Here’s how:
Data handling and security practices
CloudFactory adheres to strict data handling and security protocols, including encryption in transit and at rest, secure access controls, and regular security audits. These practices ensure that the data used to train and validate AI models is protected against unauthorized access and manipulation, contributing to the overall security and integrity of AI systems.
Quality control
CloudFactory employs rigorous quality control measures in its data annotation and processing services. By ensuring high-quality, accurately labeled data, CloudFactory helps AI developers enhance the accuracy and reliability of their models. Accurate data is crucial for training AI systems to perform as intended, reducing the risk of errors that could lead to unintended consequences.
Human-in-the-loop (HITL) oversight
CloudFactory’s HITL approach provides an effective mechanism for human oversight, allowing for the review and correction of AI outputs. This oversight is essential for maintaining the robustness of AI systems, as it enables the timely identification and rectification of inaccuracies or biases in AI decisions, ensuring that the AI systems remain aligned with their intended purpose and ethical standards.
CloudFactory is also developing a human-in-the-loop (HITL) API toolkit for model monitoring and oversight with its Accelerated Annotation labeling platform so that ML teams can seamlessly integrate automated, on-demand access to an expert workforce directly within their AI workflows.
This developer-friendly toolkit addresses the #1 challenge we hear from ML teams regarding AI in production – access to quick and efficient methods to monitor and improve their models in real-world scenarios – and supports critical tasks, such as:
- Exception handling: resolve low-confidence inferences and edge cases for production workflows.
- Model monitoring: measure and monitor the accuracy and reliability of CV models against human-verified ground truth.
- Quality assurance: Comprehensive, 100% examination of all data to provide the highest level of quality assurance.
- Model auditing: independently verify production models’ behavior against key risk frameworks from a trusted third party.
- Model improvement: analyze efficacy and identify model performance and improvements in AI models.
Expertise in secure environments
CloudFactory has experience working within secure environments required by industries such as healthcare and finance, which often deal with sensitive information and have stringent requirements for accuracy and security. This experience positions CloudFactory well to help AI developers implement the necessary security measures and protocols to protect AI systems from intentional attacks and unintentional errors.
Compliance and certification
CloudFactory's commitment to international standards for information security, such as ISO 27001, demonstrates its capability to manage information security systematically. This commitment helps AI developers meet the legislative requirements of the AI Act by ensuring that their AI systems are developed and operated within a framework that prioritizes security and data protection.
Attention to these areas helps businesses comply with the EU AI Act and builds trust with users and the broader public, which is critical for the successful adoption and integration of AI technologies into society.
By leveraging CloudFactory's expertise and capabilities in data security, quality assurance, and human oversight, AI developers can more easily address the EU AI Act's stringent requirements for high-risk AI systems, ensuring their solutions are compliant, resilient, accurate, and secure.
If you need more information about how to safely navigate through the various risks associated with the new EU AI Act, contact us and our experts will be ready to help every step of the way.



